Breaking Down Neural Networks
"Understanding neural networks, their components and varieties."
By Kavitha A
01/01/2025
In today's tech-driven world, neural networks have become the backbone of many revolutionary technologies, including image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving. Despite their widespread use, understanding how neural networks work can feel daunting. Let's break down the concept of neural networks into manageable parts, making it accessible even to those new to artificial intelligence (AI).
What is a Neural Network?
A neural network is a computational model inspired by the human brain. It consists of layers of interconnected nodes (also called neurons) that process data and make predictions or decisions. Neural networks are a key component of machine learning, a subset of AI, where systems learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed.
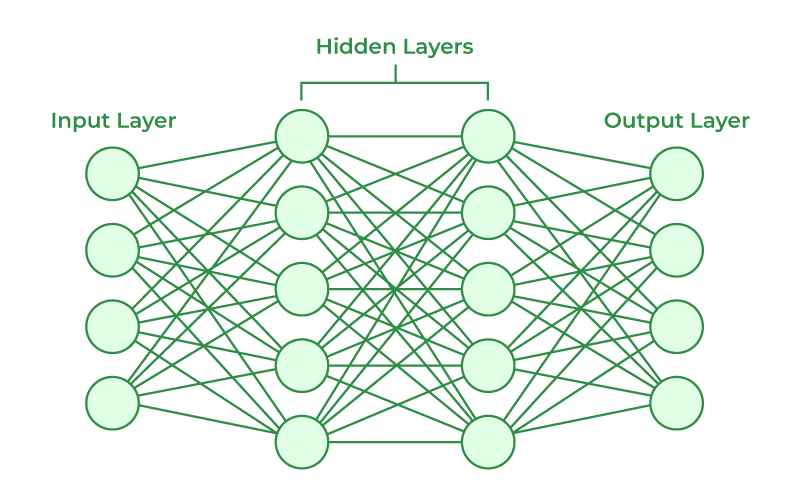
Components of Neural Networks
To understand how neural networks work, it's essential to grasp their primary components:
Input Layer
It is the first layer of nodes that receives the raw data (e.g., images, text, or numerical data) and prepares input data for the network to process.
Hidden Layers
These layers are where the magic happens. Each hidden layer consists of neurons that process input data using mathematical operations. The number of hidden layers and neurons depends on the complexity of the problem.
Output Layer
This layer produces the final result, such as a classification label (e.g., "cat" or "dog") or a numerical prediction.
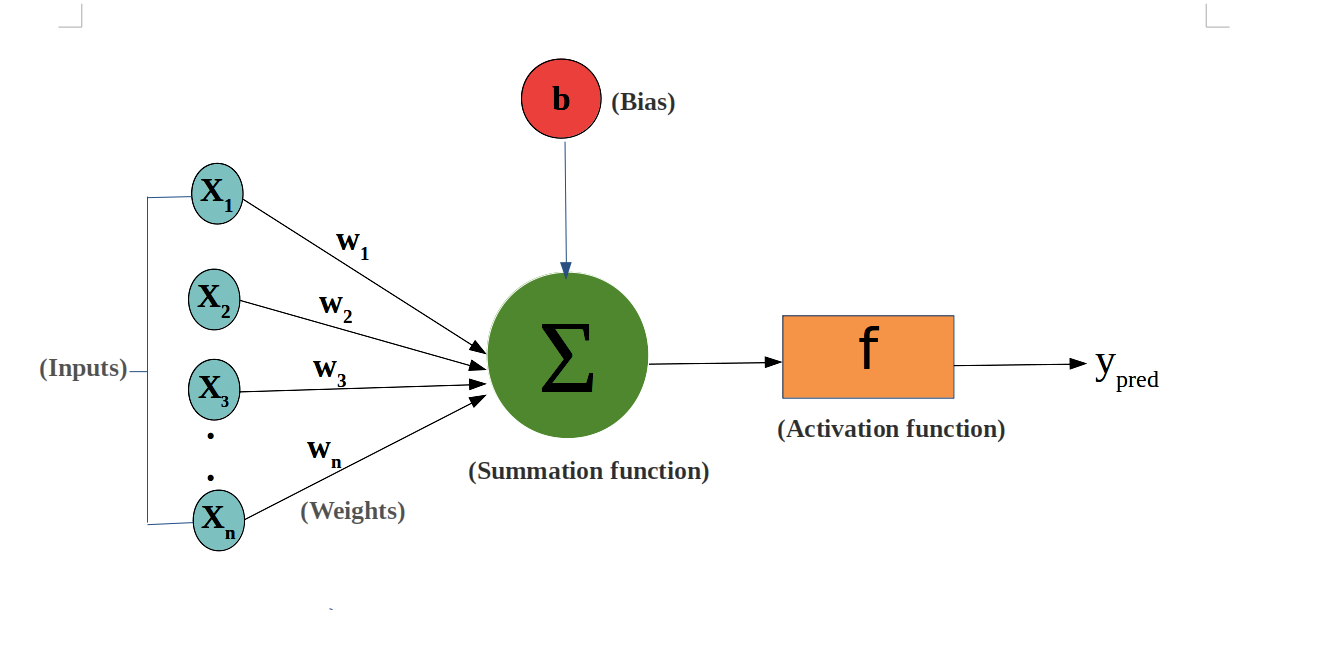
Weights and Biases
Weights determine the importance of each input, while biases help shift the activation function to improve learning.
Activation Functions
These functions introduce non-linearity to the network, enabling it to learn complex patterns. Common activation functions include ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit), sigmoid, and tanh.
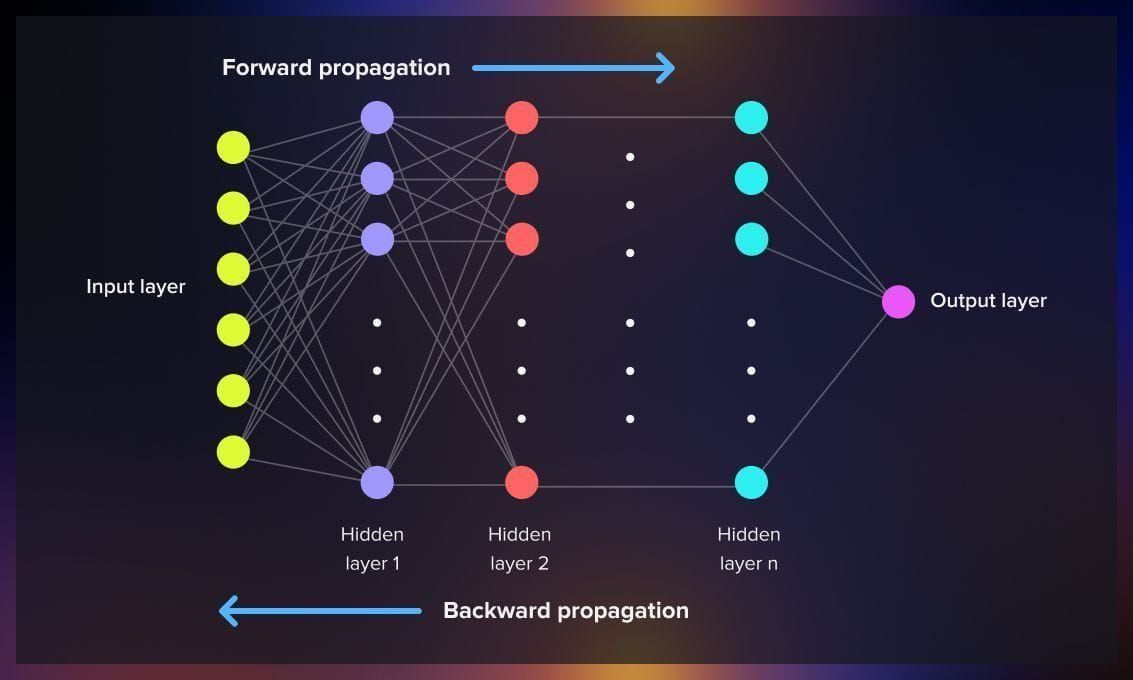
How Does a Neural Network Work?
Step 1: Forward Propagation
- Data flows from the input layer through the hidden layers to the output layer
- Each neuron receives inputs, applies weights and biases, and passes the result through an activation function
- The output of one layer becomes the input for the next layer
Step 2: Loss Calculation
- The network's output is compared to the actual target value to calculate the error, also known as the loss
- Common loss functions include Mean Squared Error (MSE) for regression tasks and Cross-Entropy Loss for classification tasks
Step 3: Backpropagation
- The network adjusts its weights and biases to minimize the loss
- Backpropagation uses a technique called gradient descent to update the weights in the direction that reduces the error
Step 4: Iterative Learning
- Steps 1 to 3 are repeated for multiple iterations (epochs) until the network's performance reaches an acceptable level
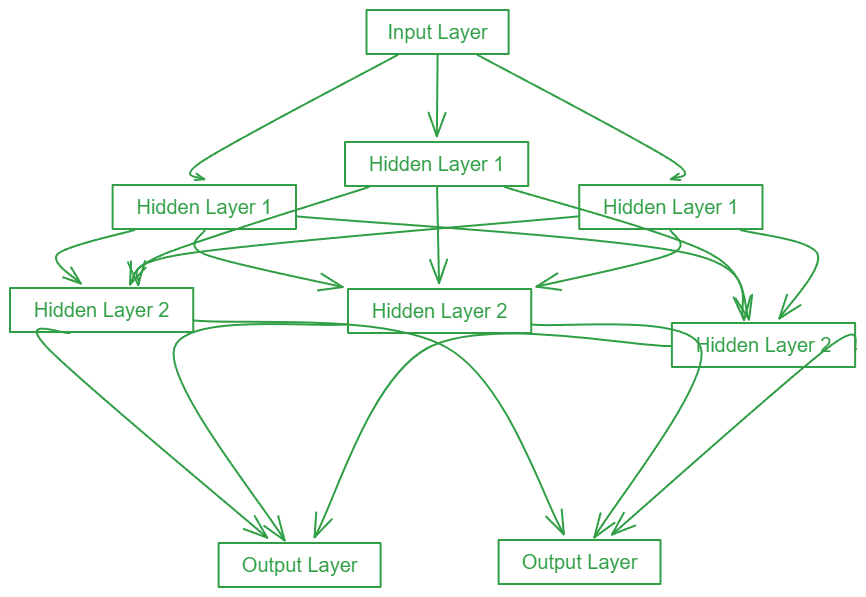
Types of Neural Networks
Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs)
It is a type of artificial neural network where connections between the nodes do not form cycles and data flows in one direction, from input to output. Ideal for simple tasks like basic classification.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
It uses deep learning to learn from data and recognize patterns. CNNs are often used to recognize objects in images, but they can also be used to classify audio, time-series, and signal data. It is a powerful tool but requires millions of labeled data points for training.
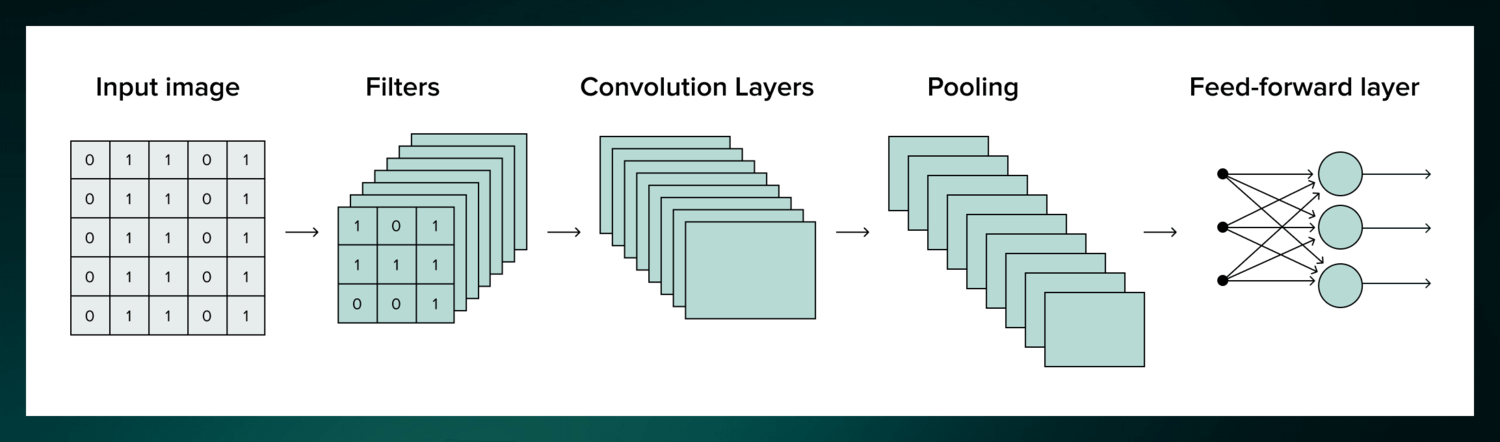
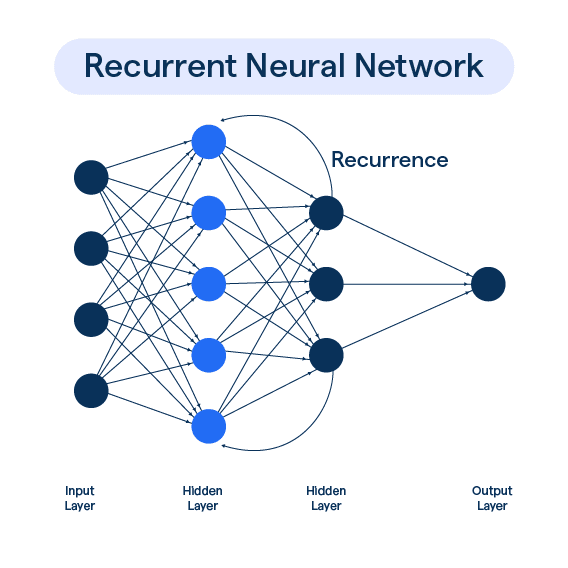
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
It is a deep learning model that is trained to process and convert sequential data input into specific sequential data output. It applies the same network to each element in a sequence, RNNs preserve and pass on relevant information, enabling them to learn temporal dependencies that conventional neural networks cannot.
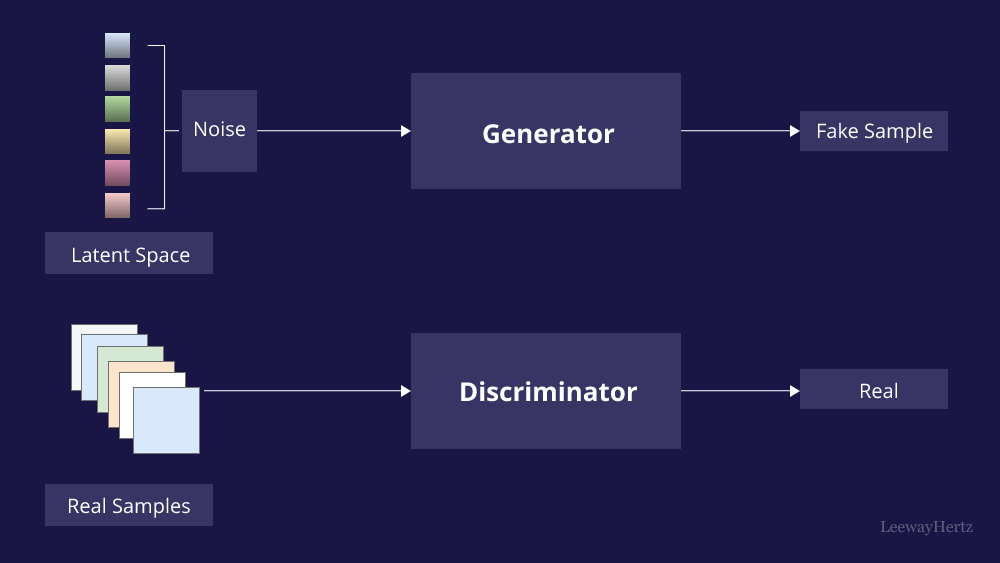
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
It is a machine learning framework that uses two neural networks to generate new data that resembles a training dataset. Generator creates new data by modifying an input data sample, while the discriminator distinguishes between real data and the generator's fake data.
Applications of Neural Networks
Neural networks have found applications across numerous industries:
- Image Recognition
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Healthcare
- Finance
- Autonomous Vehicles
- Retail
- Gaming
- Weather Forecasting
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing
Conclusion
Neural networks have transformed the landscape of AI, making it possible to tackle problems that were once considered unsolvable. By understanding their structure and working, you can appreciate the ingenuity behind these systems. As these technologies evolve, their potential applications will continue to expand, reshaping industries and improving lives. Whether you're a student, developer, or enthusiast, exploring neural networks is a journey that opens up endless possibilities for innovation and creativity.